Scientists have grown miniature brains out of stem cells from people with autism, and have found that they over-produce one type of neuron.
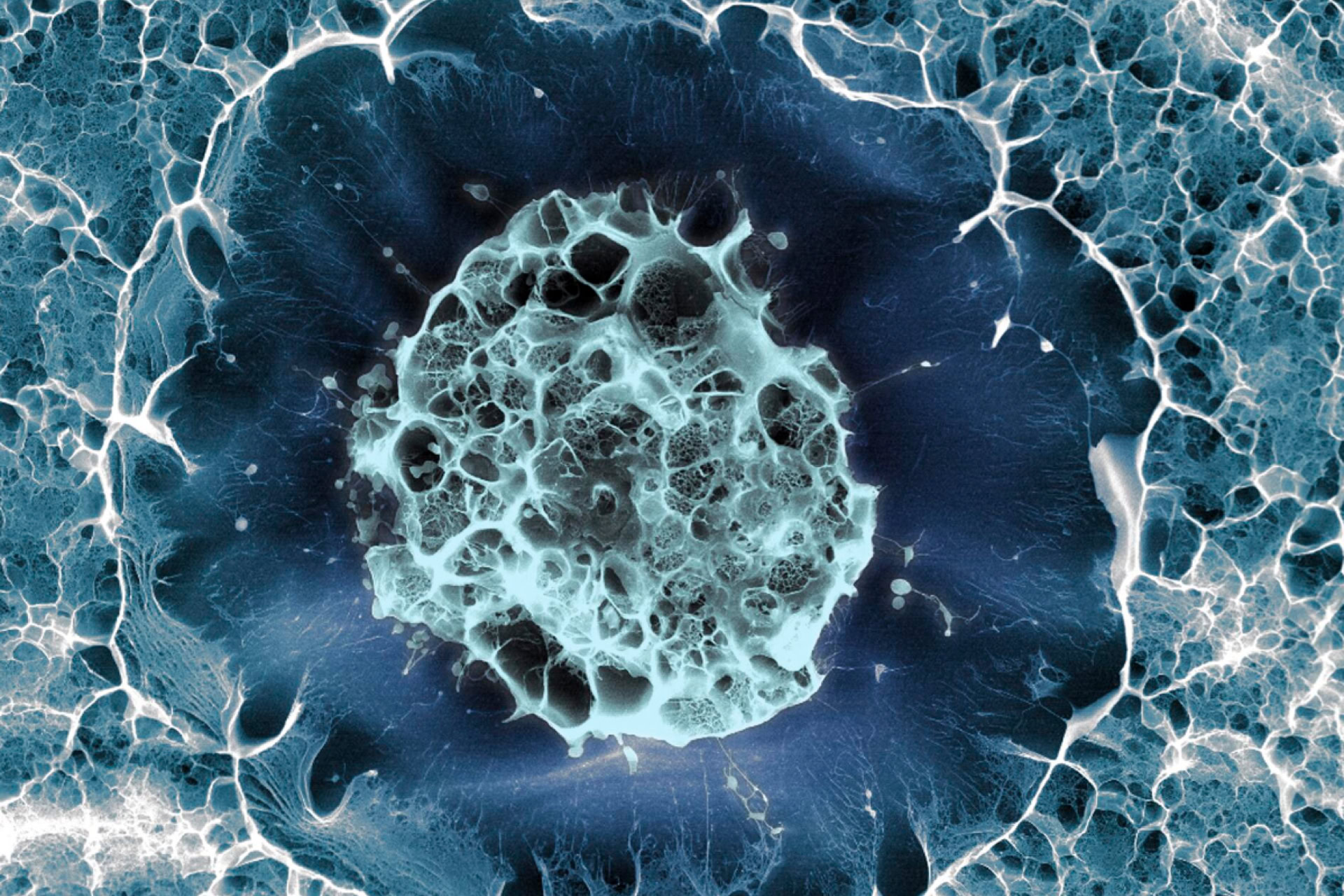
These tiny brain 'organoids' — three-dimensional clusters of cells, just a few millimetres across — mimic the brains of early fetuses and allow scientists to study early neurological development in a way that was not possible before.
Previous studies have looked at the genomes of those with autism to identify the genes that might be responsible, but 80 percent of autism cases have no clear genetic cause. This is the first study to use brain organoids to investigate the disorder, which is characterised by social and communication difficulties.
'Instead of starting from genetics, we've started with the biology of the disorder itself to try to get a window into the genome,' said Professor Flora Vaccarino of the Yale School of Medicine, senior author of the paper, which was published in Cell.
The researchers took skin cells from four adolescent males with autism and from their fathers who were unaffected by the disorder. They first induced them to become embyronic-like stem cells, and then encouraged them to grow into clusters of brain neurons. These clusters are similar the brain of a fetus during the second trimester, called the telencephalon.
'I immediately realised that this could be used to re-enact stages of neurodevelopment that were almost impossible to study in humans,' Professor Vaccarino told The Scientist.
Despite the fact that autism is a complex collection of disorders, the researchers found several clear differences between the brain organoids from the autistic boys and those from their fathers. In particular, there were more inhibitory neurons (which quieten down brain activity) compared to excitatory neurons (which amplify brain activity).
Tracing this back to the increased expression of a gene involved in early brain development — FoxG1 — the researchers were then able to restore a normal balance of inhibitory and excitatory neurons by suppressing the expression of this gene in the autistic brain organoids.
Neuroscientist Dr Alysson Muotri of the University of California, San Diego, who was not involved in the study, told The Scientist the results were impressive and surprising. 'If someone had asked me, I would have said, "You won't find anything in common, it's probably going to be a mixed bag." But no... there seems to be key things that are dysregulated in all of them.'
Professor Vaccarino is hopeful that this approach to studying autism, as well as other brain disorders, can offer new insights. 'This study speaks to the importance of using human cells [to] bring a better understanding of the pathophysiology of autism and, with that, possibly better treatments.'
Sources and References
-
Tiny Brain Clumps Offer New Clues into the Cause of Autism
-
Mini Brains Model Autism
-
Miniature brain in a dish reveals an outsized secret about autism
-
Miniature brains made from patient skin cells reveal insights into autism
-
FOXG1-Dependent Dysregulation of GABA/Glutamate Neuron Differentiation in Autism Spectrum Disorders




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.