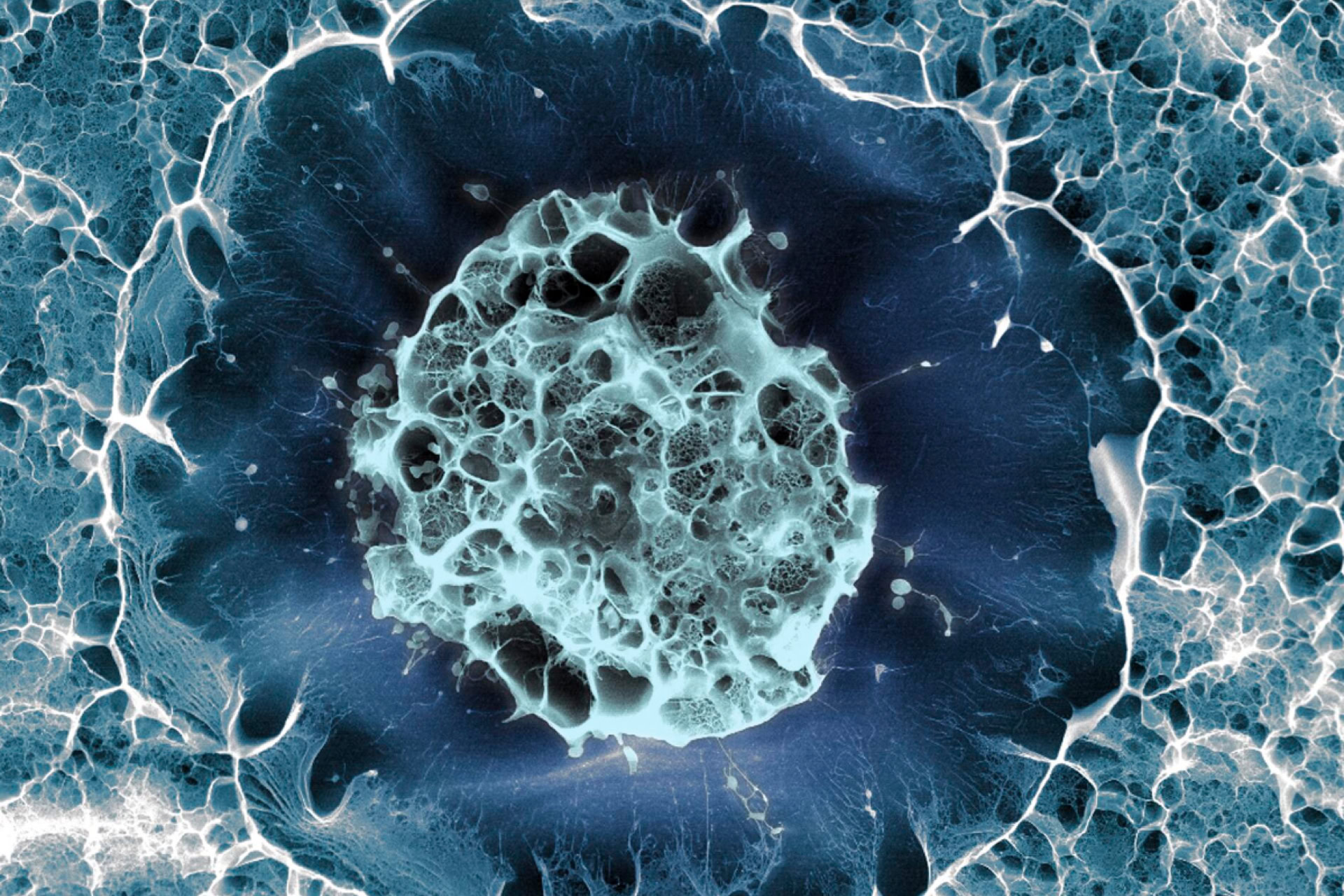
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, has been shown to infect cortical neurons and specifically destroys their synapses – the connections between brain cells that allow them to communicate with each other.
An international team of researchers, led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Sanford Consortium, used human brain organoids in their research, and further showed that an antiviral drug approved to treat hepatitis C, effectively inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication and reversed brain cell damage in the organoids.
'This work helps explain some of the neurological symptoms of COVID-19 and, more importantly, it suggests that an FDA-approved antiviral drug might be repurposed to restore infected brain cells to health and address long-term neurological outcomes of COVID-19.' said senior study author Professor Alysson Muotri.
The results have been published in PLOS Biology and a press release has been issued.