Genome editing screen finds cancer mutations faster
A genome editing technique that allows researchers to test thousands of different mutations that might affect how cancer cells behave has been developed...
CRISPR Associated Proteins are enzymes that associate with CRISPR RNAs to bind to and alter DNA or RNA target sequences.
Cas enzymes originate in bacteria and as such a wide variety of types exist. Some are used for genome editing or editing RNA.
There are also versions that have been altered in the lab to perform specific tasks. Common examples include Cas9 which makes a double-stranded break in a target DNA sequence, and Cas13 which targets RNA.
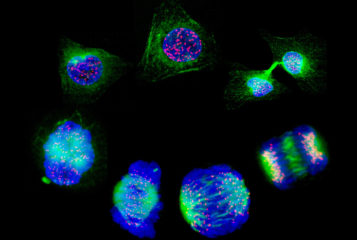
A genome editing technique that allows researchers to test thousands of different mutations that might affect how cancer cells behave has been developed...



Two potential new treatments for Alzheimer's disease using the CRISPR genome editing approach have been reported at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference, in Amsterdam, the Netherlands...


A new genome editing mechanism has been developed for the first time from a protein found in eukaryotes...

by Hannah Flynn
Cells in early human embryos are unable to effectively repair the double-stranded DNA breaks made during CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing...

by Catherine Turnbull and 1 others
A novel CRISPR-based gene therapy has been shown to reduce the level of antibiotic resistant E. coli within the gastrointestinal tract...

A CRISPR-based form of genome editing that can replace entire genes may offer a new way to treat some genetic diseases...

A newly described CRISPR-associated protein can kill infected cells by cutting all types of DNA and RNA...
BioNews, published by the Progress Educational Trust (PET), provides news and comment on genetics, assisted conception, embryo/stem cell research and related areas.

